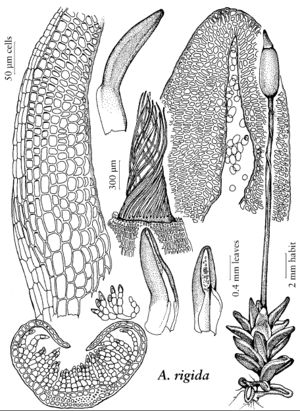
Aloina rigida var. rigida
Plants to 2.5 mm. Leaves short-lingulate to ligulate, 0.5–2.5 mm, margins entire to irregularly denticulate, differentiated at base, apex cucullate; costa subpercurrent to percurrent, filaments of 3–9 cells, cells cylindric to spheric; cells of leaf base 11–88 µm, medial and distal cells 9–40 µm, papillae none. Sexual condition dioicous. Seta 4.5–17 mm. Capsule urn ovoid-cylindric, 1.7–3.4 mm; operculum conical to subulate, long-rostrate, 1.2–1.9 mm; peristome 1200–1750 µm, strongly twisted. Spores 11–22 µm.
Phenology: Capsules mature Jun–Aug(-Oct).
Habitat: Rocks, banks, clay, sandy or gravelly soil in deserts, plains or conifer forests
Elevation: moderate to high elevations (1000-3000 m)
Distribution
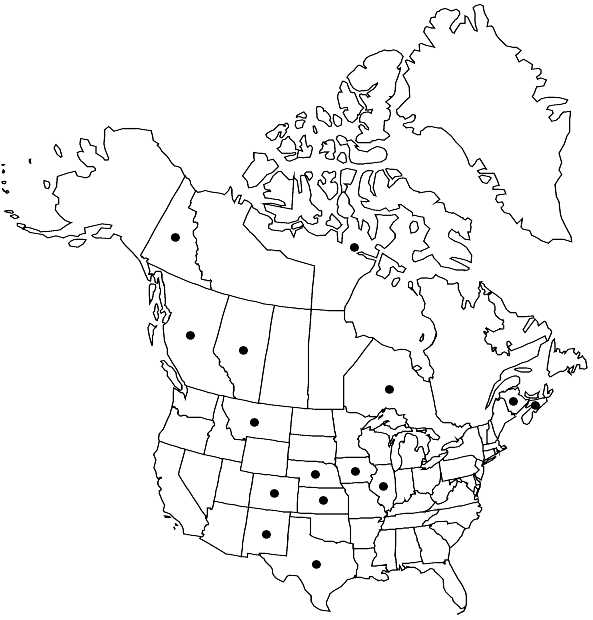
Alta., B.C., N.B., N.S., Nunavut, Ont., Yukon, Colo., Ill., Iowa, Kans., Mont., Nebr., N.Mex., Tex., Mexico (Nuevo León, Querétaro, Zacatecas), South America, Europe, Asia, Africa.
Discussion
The ovoid-cylindrical capsule with a long peristome and long-rostrate operculum as well as the differentiated basal leaf margins are the distinguishing features of var. rigida. Despite recent reports from California, this species has not been confirmed from that state.
Selected References
None.