Lygodesmia grandiflora var. dianthopsis
Great Basin Naturalist 43: 314. 1983.
Plants (5–)20–60 cm. Stems erect or ascending, purple proximally, slender, simple or sparingly branched from bases or distally, smooth (glabrous or tomentulose). Leaves: (proximalmost reduced to scales at ground level) proximal blades linear, 50–110 × 2–6 mm, ± lax; distal linear, less than 10 mm, distally reduced to linear scales. Heads 2–13, in loose, corymbiform arrays. Involucres subcylindric, 15–22 × 4–5 mm, apices narrow. Phyllaries 5–6. Florets 5; corollas purple to lavender or white. Cypselae 12–19 mm, abaxial faces smooth, adaxial distinctly rugose, weakly sulcate. 2n = 18.
Phenology: Flowering Jun–Jul.
Habitat: Sandy and gravelly soils in juniper-pinyon scrub, open fields, sandy roadsides
Elevation: 1300–2500 m
Distribution
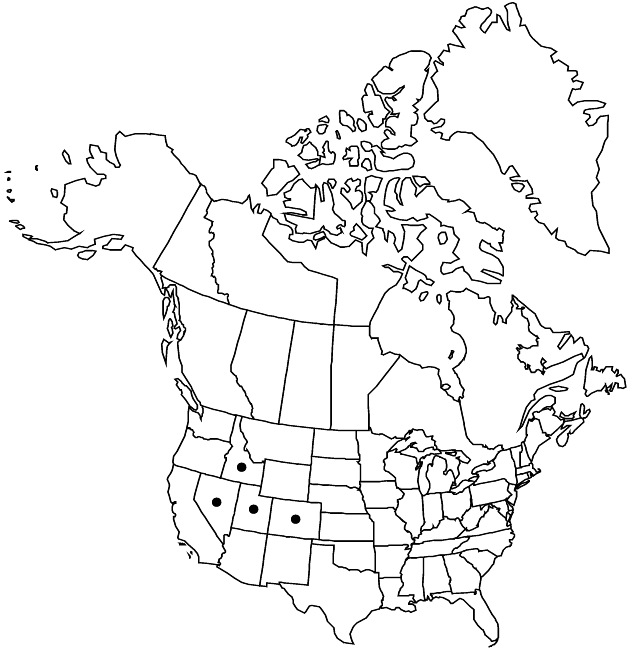
Colo., Idaho, Nev., Utah.
Discussion
Variety dianthopsis is recognized by its slender, erect, leafy stems, purplish at base, persistent cauline leaves, phyllaries with appendages, 5–6 florets per head, and distinctive rugose-roughened cypselae. It usually is taller than var. arizonica. The stems and leaves are occasionally sparsely tomentulose.
Selected References
None.