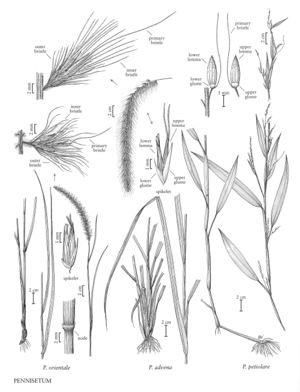
Pennisetum orientale
Plants perennial; rhizomatous. Culms 50-200 cm, erect, pubescent beneath the panicle; nodes pubescent. Leaves green or glaucous; sheaths antrorsely scabridulous, mostly glabrous, margins ciliate; ligules 1-1.7 mm; blades 25-50 cm long, 3-9 mm wide, flat, antrorsely scabridulous, glabrous or pubescent, margins ciliate or glabrous basally, midvein not noticeably thickened. Panicles 11.5-37.3 cm long, 35-50 mm wide, fully exerted from the sheaths, erect to slightly arching, white (sometimes purplish-tinged); rachises terete, pubescent. Fascicles 5-12 per cm; fascicle axes 1-6 mm, with 1-10 spikelets; outer bristles 0-24, 0.8-9.6 mm, terete, scabrous; inner bristles 6-20, 5.6-17.5 mm, ciliate; primary bristles 12.2-23.8 mm, ciliate, noticeably longer than the other bristles. Spikelets 5.6-6.7 mm; pedicels 0.1-0.2 mm; lower glumes 1-2.2 mm, veinless; upper glumes 3.1-5.5 mm, 1-3-veined; lower florets staminate; lower lemmas 5.2-6.5 mm, 4-6-veined; lower paleas 3.8-5 mm; anthers 2.3-3 mm; upper florets not disarticulating at maturity; upper lemmas 5.2-6.2 mm, margins glabrous, 5-veined; upper paleas bifid, teeth 0.3-0.8 mm; anthers 1.9-2.9 mm. Caryopses concealed by the lemma and palea at maturity. 2n = 18, 27, 36, 45, 54.
Discussion
Pennisetum orientale is native from North Africa to India. It is grown as an ornamental in the Flora region, but has potential as a forage species.
Selected References
None.