Philadelphus coronarius
Sp. Pl. 1: 470. 1753.
Shrubs, 10–40 dm. Stems erect to ascending, green, older stems brown, branched, glabrous or sparsely strigose (especially at nodes); bark deciduous, exfoliating or flaking, reddish; branches erect to arching; axillary buds hidden in pouches, sometimes apex exposed, especially on vigorous sprout-shoots. Leaves: petiole 1–6 mm; blade usually broadly lanceolate to broadly ovate, or narrowly to broadly elliptic, rarely narrowly lanceolate in horticultural forms, 3–10 × 2–6 cm, larger blades usually greater than 6 × 2.5 cm, base narrowly cuneate to rounded, margins entire to irregularly or regularly serrate, crenate, or dentate, plane, abaxial surface glabrous or sparsely strigose, hairs usually appressed-ascending, not twisted, main vein axils often moderately to densely strigose-tomentose, main veins sometimes sparsely strigose, secondary and tertiary veins rarely sparsely strigose, adaxial surface glabrous or sparsely strigose, especially near base and margins. Inflorescences cymose racemes, 5–7(–9)-flowered, proximal 2 flowers often in axils of nearly normal to much reduced (bracteal) leaves. Pedicels 3–20 mm, glabrous or sparsely strigose. Flowers: hypanthium glabrous or sparsely strigose to villous; sepals ovate, ovate-lanceolate, or triangular, 4–8 × 2.5–5 mm, apex acute to acuminate, abaxial surface glabrous or sparsely strigose, adaxial surface glabrous except densely villosulous distally; petals white to cream, oblong, obovate, or orbiculate, 5–25 × 5–22 mm; stamens 20–50; filaments distinct, 4–9 mm; anthers 1–1.5 × 0.7–1 mm; styles 4, connate proximally, cylindric, 7–10 mm, lobes 3–8 × 0.3–0.9 mm; stigmatic surfaces 1–4 mm. Capsules obconic to obovoid, 7–11 × 4–7 mm. Seeds caudate, 3 mm. 2n = 26.
Phenology: Flowering May–Jul; fruiting Jul–Sep.
Habitat: Old home sites, suburban woodlands, stream banks.
Elevation: 0–1000 m.
Distribution
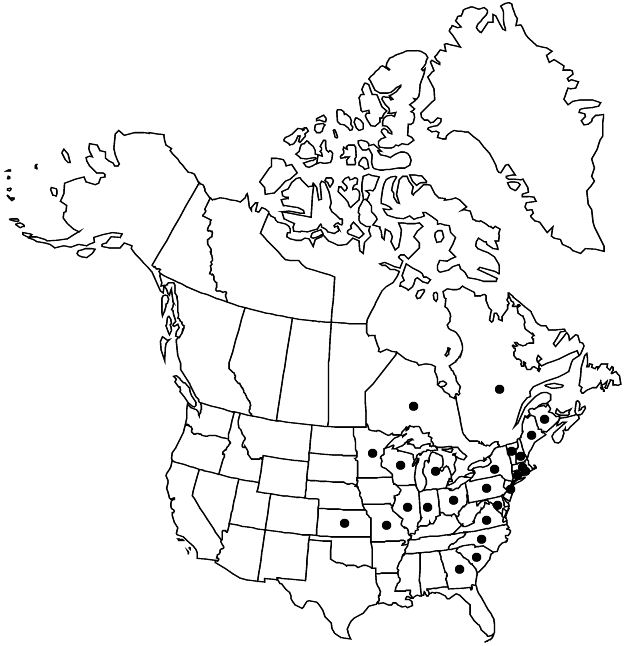
Introduced; N.B., Ont., Que., Conn., Ga., Ill., Ind., Kans., Maine, Md., Mass., Mich., Minn., Mo., N.H., N.J., N.Y., N.C., Ohio, Pa., R.I., S.C., Vt., Va., Wis., Eurasia.
Discussion
Philadelphus coronarius is likely to occur in states and provinces other than those listed because it is widely cultivated and may escape.
Philadelphus caucasicus is here provisionally considered to be a synonym of P. coronarius, though further study in their native area is needed. Both are native in the Caucasus region, according to Hu S. Y. (1954–1956), and the only character by which she separated them (vestiture on the disc and style) is variable in other taxa in the genus and seems of doubtful taxonomic meaning in the case of these two sympatric, putative taxa. The native distribution of P. coronarius is unclear. Hu considered it native in southern Europe and the Caucasus Mountains of southern Russia, Armenia, Georgia, and Azerbaijan. D. A. Webb (1993) emphasized the uncertainty of its native range, mentioning that stations in Europe where it is undoubtedly native are very few; it may be that this species is native only in the Caucasus and was brought early to Europe for ornament.
Selected References
None.