Polygonum patulum
Fl. Taur.-Caucas. 1: 304. 1808.
Plants green or bluish green, heterophyllous. Stems mostly ascending or erect, branched from base, not wiry, 20–80 cm. Leaves: ocrea 7–9 mm, proximal part cylindic, distal part disintegrating into straight fibers; petiole 0.2–1 mm; blade green or bluish green, linear to lanceolate, 25–40 × 4–8 mm, margins flat, apex acute; stem leaves 2–4 times as long as branch leaves; distal leaves abruptly reduced and not overtopping flowers (shorter than or equaling flowers). Inflorescences axillary and terminal, spikelike; cymes aggregated at tips of stems and branches, 1–3-flowered. Pedicels enclosed in ocreae, 1.5–2 mm. Flowers closed or semi-open; perianth 2.2–3 mm; tube 15–30% of perianth length; tepals overlapping, green with white to pink margins, petaloid, not keeled, oblong, cucullate; veins branched; stamens 8. Achenes slightly exserted from perianth, light brown to dark brown, ovate, 3-gonous, 2–2.3(–2.8) mm, faces subequal, concave, apex not beaked, edges concave, dull, striate-tubercled; late-season achenes uncommon, 2.5–4 mm.
Phenology: Flowering Jul–Oct.
Habitat: Waste places
Elevation: 0-800 m
Distribution
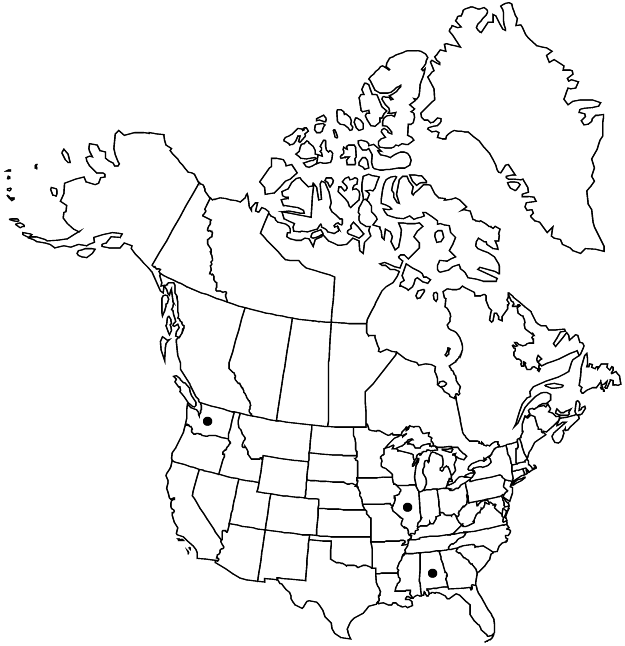
Introduced; Ala., Ill., Wash., Eurasia, n Africa.
Discussion
The name Polygonum patulum has been misapplied to a distinctive form of P. ramosissimum in saline marshes in California (M. Costea and F. J. Tardif 2003b).
Selected References
None.