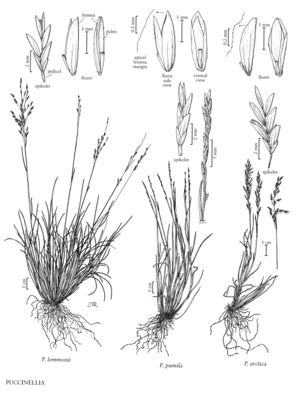
Puccinellia lemmonii
Plants perennial; cespitose, not mat-forming. Culms 5-40 cm, usually erect. Leaves basally concentrated; ligules 0.8-2.2 mm, obtuse to acute, mostly entire, sometimes slightly erose; blades involute, 1.2-1.9 mm wide when flattened. Panicles 2-18 cm, compact to diffuse at maturity, lower branches ascending to descending, usually spikelet-bearing to the base; pedicels scabrous, lacking tumid epidermal cells. Spikelets 3.5-8 mm, with 2-6 florets. Glumes rounded over the back, veins obscure, apices acute to obtuse; lower glumes 0.7-1.5 mm; upper glumes 1.4-3 mm; calluses with a few hairs; lemmas 2.4-4 mm, herbaceous, mostly smooth, usually glabrous, sometimes with a few hairs near the base, principally along the veins, backs usually rounded, sometimes weakly keeled distally, 5-veined, veins obscure, midveins often slightly scabrous and prominent in the distal 1/2, often extending to the apical margins, lateral veins not extending to the margins, apical margins ranging from smooth to scabrous, entire, not white, apices acute, entire; palea veins glabrous or shortly ciliate proximally, uniformly scabrous distally; anthers 1-2 mm. 2n = 14.
Distribution
Wash., Calif., Oreg., Mont., Wyo., Idaho, Nev.
Discussion
Puccinellia lemmonii grows in non-littoral saline environments in the western portion of the contiguous United States. Reports from Saskatchewan are probably based on depauperate specimens of P. nuttalliana.
Selected References
None.