Difference between revisions of "Anaphalis margaritacea"
Gen. Pl. 2: 303. 1873.
FNA>Volume Importer |
FNA>Volume Importer |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
|name=Anaphalis margaritacea var. occidentalis | |name=Anaphalis margaritacea var. occidentalis | ||
|authority=Greene | |authority=Greene | ||
| − | }}{{Treatment/ID/Synonym | + | }} {{Treatment/ID/Synonym |
|name=Anaphalis margaritacea var. subalpina | |name=Anaphalis margaritacea var. subalpina | ||
|authority=(A. Gray) A. Gray | |authority=(A. Gray) A. Gray | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
|elevation=0–3200 m | |elevation=0–3200 m | ||
|distribution=St. Pierre and Miquelon;Alta.;B.C. ;Man.;N.B.;Nfld. and Labr.;N.W.T.;N.S.;Ont.;P.E.I. Que.;Sask.;Yukon;Alaska;Ariz.;Ark.;Calif.;Colo.;Conn.;Del.;Idaho;Ill.;Ind.;Iowa;Ky.;Maine;Md.;Mass.;Mich.;Minn.;Mont.;Nebr.;Nev.;N.H.;N.J.;N.Mex.;N.Y.;N.C.;Ohio;Oreg.;Pa.;R.I.;S.Dak.;Tenn.;Tex.;Utah;Vt.;Va.;Wash.;W.Va.;Wis.;Wyo.;Mexico (Baja California);Asia;introduced in Europe. | |distribution=St. Pierre and Miquelon;Alta.;B.C. ;Man.;N.B.;Nfld. and Labr.;N.W.T.;N.S.;Ont.;P.E.I. Que.;Sask.;Yukon;Alaska;Ariz.;Ark.;Calif.;Colo.;Conn.;Del.;Idaho;Ill.;Ind.;Iowa;Ky.;Maine;Md.;Mass.;Mich.;Minn.;Mont.;Nebr.;Nev.;N.H.;N.J.;N.Mex.;N.Y.;N.C.;Ohio;Oreg.;Pa.;R.I.;S.Dak.;Tenn.;Tex.;Utah;Vt.;Va.;Wash.;W.Va.;Wis.;Wyo.;Mexico (Baja California);Asia;introduced in Europe. | ||
| − | |discussion=<p>Anaphalis margaretacea was widely planted as an ornamental and escaped. It apparently naturalized from its native range in both Asia and North America; it is cultivated and naturalized in Europe.</p><!-- | + | |discussion=<p><i>Anaphalis</i> margaretacea was widely planted as an ornamental and escaped. It apparently naturalized from its native range in both Asia and North America; it is cultivated and naturalized in Europe.</p><!-- |
| − | --><p>Anaphalis margaritacea has the aspect of Pseudognaphalium; it differs in being subdioecious (polygamo-dioecious; the heads either staminate or primarily pistillate) and in its distinctive cypselar vestiture. It is further recognized by its combination of rhizomatous habit, subclasping-decurrent, bicolor, revolute leaves, and distally white phyllaries. Segregate species and varieties have been described among the North American plants (in addition to the two cited above), based on variation in habit, vestiture, and leaf morphology and density, but the variants appear to be more like a complex series of ecotypes rather than broader evolutionary entities.</p> | + | --><p><i>Anaphalis margaritacea</i> has the aspect of <i>Pseudognaphalium</i>; it differs in being subdioecious (polygamo-dioecious; the heads either staminate or primarily pistillate) and in its distinctive cypselar vestiture. It is further recognized by its combination of rhizomatous habit, subclasping-decurrent, bicolor, revolute leaves, and distally white phyllaries. Segregate species and varieties have been described among the North American plants (in addition to the two cited above), based on variation in habit, vestiture, and leaf morphology and density, but the variants appear to be more like a complex series of ecotypes rather than broader evolutionary entities.</p> |
|tables= | |tables= | ||
|references= | |references= | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
|publication year=1873 | |publication year=1873 | ||
|special status= | |special status= | ||
| − | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/ | + | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/8f726806613d60c220dc4493de13607dd3150896/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V19-20-21/V19_704.xml |
|tribe=Asteraceae tribe Gnaphalieae | |tribe=Asteraceae tribe Gnaphalieae | ||
|genus=Anaphalis | |genus=Anaphalis | ||
Revision as of 16:14, 18 September 2019
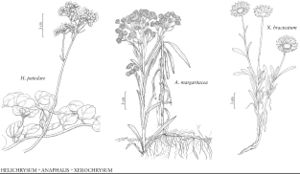
Perennials; rhizomes relatively slender. Stems white, densely and closely tomentose, not glandular. Leaf blades 1–3-nerved, 3–10(–15) cm, bases subclasping, decurrent, margins revolute, abaxial faces tomentose or glabrescent (proximal leaves), not glandular or very sparsely and inconspicuously glandular, adaxial faces green, glabrate. Involucres 5–7 × 6–8(–10) mm. Phyllaries ovate to nearly linear (innermost), subequal to unequal, apices white, opaque. Cypselae 0.5–1 mm, bases constricted into stipiform carpopodia. 2n = 28.
Phenology: Flowering Jul–Oct (sporadically longer).
Habitat: Dry woods, often with aspen or mixed conifer-hardwood, borders and trails, dunes, fields, roadsides, other open, often disturbed sites
Elevation: 0–3200 m
Distribution
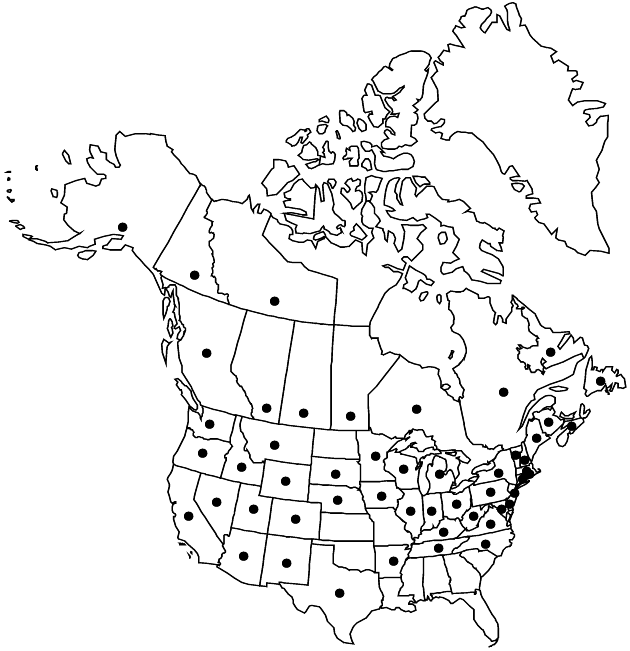
St. Pierre and Miquelon, Alta., B.C., Man., N.B., Nfld. and Labr., N.W.T., N.S., Ont., P.E.I. Que., Sask., Yukon, Alaska, Ariz., Ark., Calif., Colo., Conn., Del., Idaho, Ill., Ind., Iowa, Ky., Maine, Md., Mass., Mich., Minn., Mont., Nebr., Nev., N.H., N.J., N.Mex., N.Y., N.C., Ohio, Oreg., Pa., R.I., S.Dak., Tenn., Tex., Utah, Vt., Va., Wash., W.Va., Wis., Wyo., Mexico (Baja California), Asia, introduced in Europe.
Discussion
Anaphalis margaretacea was widely planted as an ornamental and escaped. It apparently naturalized from its native range in both Asia and North America; it is cultivated and naturalized in Europe.
Anaphalis margaritacea has the aspect of Pseudognaphalium; it differs in being subdioecious (polygamo-dioecious; the heads either staminate or primarily pistillate) and in its distinctive cypselar vestiture. It is further recognized by its combination of rhizomatous habit, subclasping-decurrent, bicolor, revolute leaves, and distally white phyllaries. Segregate species and varieties have been described among the North American plants (in addition to the two cited above), based on variation in habit, vestiture, and leaf morphology and density, but the variants appear to be more like a complex series of ecotypes rather than broader evolutionary entities.
Selected References
None.