Difference between revisions of "Ancistrocactus brevihamatus"
Cact. 4: 5. 1923.
FNA>Volume Importer |
imported>Volume Importer |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
}} | }} | ||
|common_names=Short-spined fishhook cactus;Tobusch cactus | |common_names=Short-spined fishhook cactus;Tobusch cactus | ||
| − | |basionyms={{Treatment/ID/ | + | |basionyms={{Treatment/ID/Basionym |
|name=Echinocactus brevihamatus | |name=Echinocactus brevihamatus | ||
|authority=Engelmann | |authority=Engelmann | ||
| + | |rank=species | ||
| + | |publication_title=Proc. Amer. Acad. Arts. | ||
| + | |publication_place=3: 271. 1856 | ||
}} | }} | ||
|synonyms={{Treatment/ID/Synonym | |synonyms={{Treatment/ID/Synonym | ||
|name=Ancistrocactus tobuschii | |name=Ancistrocactus tobuschii | ||
|authority=(W. T. Marshal l) W. T. Marshall ex Backeberg | |authority=(W. T. Marshal l) W. T. Marshall ex Backeberg | ||
| − | }}{{Treatment/ID/Synonym | + | |rank=species |
| + | }} {{Treatment/ID/Synonym | ||
|name=Sclerocactus brevihamatus | |name=Sclerocactus brevihamatus | ||
|authority=(Engelmann) D. R. Hunt | |authority=(Engelmann) D. R. Hunt | ||
| − | }}{{Treatment/ID/Synonym | + | |rank=species |
| + | }} {{Treatment/ID/Synonym | ||
|name=Sclerocactus brevihamatus subsp. tobuschii | |name=Sclerocactus brevihamatus subsp. tobuschii | ||
|authority=(W. T. Marshall) N. P. Taylor | |authority=(W. T. Marshall) N. P. Taylor | ||
| + | |rank=subspecies | ||
}} | }} | ||
|hierarchy=Cactaceae;Cactaceae subfam. Cactoideae;Ancistrocactus;Ancistrocactus brevihamatus | |hierarchy=Cactaceae;Cactaceae subfam. Cactoideae;Ancistrocactus;Ancistrocactus brevihamatus | ||
| Line 29: | Line 35: | ||
}}<!-- | }}<!-- | ||
| − | --><span class="statement" id="st- | + | --><span class="statement" id="st-undefined" data-properties=""><b>Plants </b>unbranched, deep-seated in substrate when young, inconspicuous. <b>Roots</b> diffuse or vertical, short, conic, cylindric, or hemispheric taproots, junction with stem obscure or inconspicuous. <b>Stems</b> spheric (to obconic or subcylindric in very old plants), flat-topped (in deep-seated young plants), (3–)4.5–10(–15) × (1.5–)4.5–8(–15) cm. <b>Spines</b>: radial spines 7–14(–18) per areole, opaque, yellowish to tan, tips yellow-brown to dark brown, turning gray, longest radial spines (5–)10–18(–29) × 0.1–0.5 mm; central spines (1–)4(–5) per areole; abaxial central spine 1 per areole, hooked (absent on immature plants and youngest adults), ± terete, angled, ridged, or dorsiventrally flattened, generally yellowish brown, rust, or dark brown, paler on abaxial surface, 7–43 × 0.4–1.5 mm; adaxial central spines (2–)3–4 per areole, erect, straight or weakly curved, adaxial surface flat (to 2 times as wide as thick), pale yellowish to gray or tan with dark tips, 1–2 times length of hooked spine (to at least 65 mm), to 1.1 mm wide. <b>Flowers</b>: inner tepals whitish, bright pink, or bright yellow, often pinkish brown or olive green with reddish brown midstripes. <b>Fruits</b> 8–25(–30) × 6–13 mm.</span><!-- |
-->{{Treatment/Body | -->{{Treatment/Body | ||
| + | |phenology=Flowering Jan–Mar. | ||
|habitat=Tamaulipan thorn scrub, Chihuahuan desert scrub, sparse grasslands, oak and juniper woodlands, creosotebush flats, sedimentary substrates including limestone [and gypsum in Mexico], usually not on steep slopes, rocky to gravelly soils | |habitat=Tamaulipan thorn scrub, Chihuahuan desert scrub, sparse grasslands, oak and juniper woodlands, creosotebush flats, sedimentary substrates including limestone [and gypsum in Mexico], usually not on steep slopes, rocky to gravelly soils | ||
|elevation=300-1300 m | |elevation=300-1300 m | ||
|distribution=Tex.;Mexico (Coahuila;Nuevo León). | |distribution=Tex.;Mexico (Coahuila;Nuevo León). | ||
| − | |discussion=<p>Without its smaller flowers, indehiscent fruits, and different seeds, Ancistrocactus brevihamatus is deceptively similar to certain species in the related genus Sclerocactus.</p><!-- | + | |discussion=<p>Without its smaller flowers, indehiscent fruits, and different seeds, <i>Ancistrocactus brevihamatus</i> is deceptively similar to certain species in the related genus <i>Sclerocactus</i>.</p><!-- |
| − | --><p>Ancistrocactus tobuschii pertains to the north-easternmost populations, from typical A. brevihamatus by yellow flowers, rarely with a hint of pink (pinkish, greenish, or brownish in A. brevihamatus), smaller stems and fruits, and thinner, more delicate and yellow spines. All of those characteristics, sometimes considered diagnostic for A. tobuschii, are unsatisfactory. The oldest plants of A. tobuschii are especially similar to A. brevihamatus, but A. tobuschii occupies marginal habitat and seldom survives long. Varietal status may be warranted for this and at least two other ecogeographical races within the species.</p> | + | --><p><i>Ancistrocactus</i> tobuschii pertains to the north-easternmost populations, from typical <i>A. brevihamatus</i> by yellow flowers, rarely with a hint of pink (pinkish, greenish, or brownish in <i>A. brevihamatus</i>), smaller stems and fruits, and thinner, more delicate and yellow spines. All of those characteristics, sometimes considered diagnostic for A. tobuschii, are unsatisfactory. The oldest plants of A. tobuschii are especially similar to <i>A. brevihamatus</i>, but A. tobuschii occupies marginal habitat and seldom survives long. Varietal status may be warranted for this and at least two other ecogeographical races within the species.</p> |
|tables= | |tables= | ||
|references= | |references= | ||
| Line 45: | Line 52: | ||
-->{{#Taxon: | -->{{#Taxon: | ||
name=Ancistrocactus brevihamatus | name=Ancistrocactus brevihamatus | ||
| − | |||
|authority=(Engelmann) Britton & Rose | |authority=(Engelmann) Britton & Rose | ||
|rank=species | |rank=species | ||
| Line 52: | Line 58: | ||
|basionyms=Echinocactus brevihamatus | |basionyms=Echinocactus brevihamatus | ||
|family=Cactaceae | |family=Cactaceae | ||
| + | |phenology=Flowering Jan–Mar. | ||
|habitat=Tamaulipan thorn scrub, Chihuahuan desert scrub, sparse grasslands, oak and juniper woodlands, creosotebush flats, sedimentary substrates including limestone [and gypsum in Mexico], usually not on steep slopes, rocky to gravelly soils | |habitat=Tamaulipan thorn scrub, Chihuahuan desert scrub, sparse grasslands, oak and juniper woodlands, creosotebush flats, sedimentary substrates including limestone [and gypsum in Mexico], usually not on steep slopes, rocky to gravelly soils | ||
|elevation=300-1300 m | |elevation=300-1300 m | ||
| Line 59: | Line 66: | ||
|publication year=1923 | |publication year=1923 | ||
|special status= | |special status= | ||
| − | |source xml=https:// | + | |source xml=https://bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation/src/2e0870ddd59836b60bcf96646a41e87ea5a5943a/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V4/V4_391.xml |
|subfamily=Cactaceae subfam. Cactoideae | |subfamily=Cactaceae subfam. Cactoideae | ||
|genus=Ancistrocactus | |genus=Ancistrocactus | ||
|species=Ancistrocactus brevihamatus | |species=Ancistrocactus brevihamatus | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
}}<!-- | }}<!-- | ||
-->[[Category:Treatment]][[Category:Ancistrocactus]] | -->[[Category:Treatment]][[Category:Ancistrocactus]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:58, 5 November 2020
Plants unbranched, deep-seated in substrate when young, inconspicuous. Roots diffuse or vertical, short, conic, cylindric, or hemispheric taproots, junction with stem obscure or inconspicuous. Stems spheric (to obconic or subcylindric in very old plants), flat-topped (in deep-seated young plants), (3–)4.5–10(–15) × (1.5–)4.5–8(–15) cm. Spines: radial spines 7–14(–18) per areole, opaque, yellowish to tan, tips yellow-brown to dark brown, turning gray, longest radial spines (5–)10–18(–29) × 0.1–0.5 mm; central spines (1–)4(–5) per areole; abaxial central spine 1 per areole, hooked (absent on immature plants and youngest adults), ± terete, angled, ridged, or dorsiventrally flattened, generally yellowish brown, rust, or dark brown, paler on abaxial surface, 7–43 × 0.4–1.5 mm; adaxial central spines (2–)3–4 per areole, erect, straight or weakly curved, adaxial surface flat (to 2 times as wide as thick), pale yellowish to gray or tan with dark tips, 1–2 times length of hooked spine (to at least 65 mm), to 1.1 mm wide. Flowers: inner tepals whitish, bright pink, or bright yellow, often pinkish brown or olive green with reddish brown midstripes. Fruits 8–25(–30) × 6–13 mm.
Phenology: Flowering Jan–Mar.
Habitat: Tamaulipan thorn scrub, Chihuahuan desert scrub, sparse grasslands, oak and juniper woodlands, creosotebush flats, sedimentary substrates including limestone [and gypsum in Mexico], usually not on steep slopes, rocky to gravelly soils
Elevation: 300-1300 m
Distribution
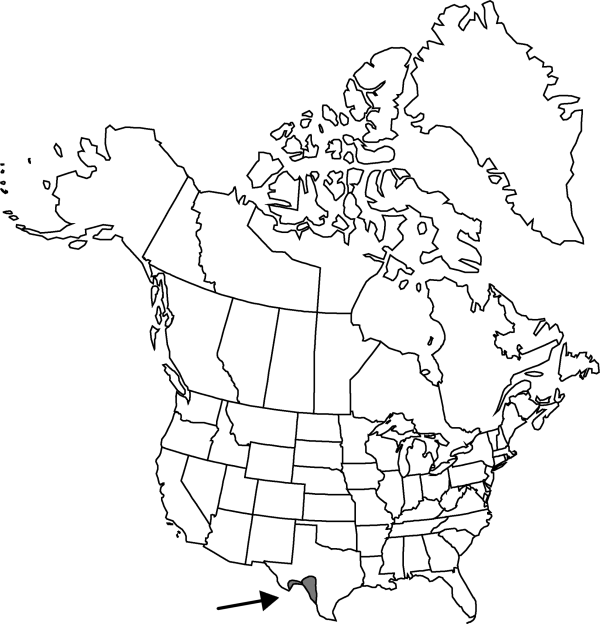
Tex., Mexico (Coahuila, Nuevo León).
Discussion
Without its smaller flowers, indehiscent fruits, and different seeds, Ancistrocactus brevihamatus is deceptively similar to certain species in the related genus Sclerocactus.
Ancistrocactus tobuschii pertains to the north-easternmost populations, from typical A. brevihamatus by yellow flowers, rarely with a hint of pink (pinkish, greenish, or brownish in A. brevihamatus), smaller stems and fruits, and thinner, more delicate and yellow spines. All of those characteristics, sometimes considered diagnostic for A. tobuschii, are unsatisfactory. The oldest plants of A. tobuschii are especially similar to A. brevihamatus, but A. tobuschii occupies marginal habitat and seldom survives long. Varietal status may be warranted for this and at least two other ecogeographical races within the species.
Selected References
None.