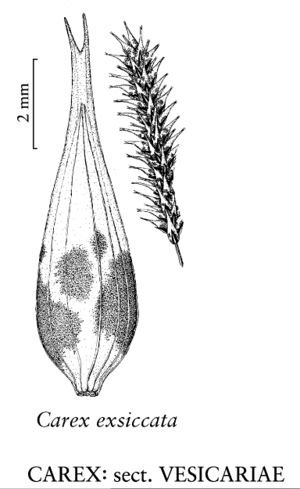
Difference between revisions of "Carex exsiccata"
Mem. Torrey Bot. Club 1: 6. 1889.
FNA>Volume Importer |
FNA>Volume Importer |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
|name=Carex vesicaria var. major | |name=Carex vesicaria var. major | ||
|authority=Boott | |authority=Boott | ||
| + | |rank=variety | ||
|publication_title=in W. J. Hooker, Fl. Bor.-Amer. | |publication_title=in W. J. Hooker, Fl. Bor.-Amer. | ||
|publication_place=2: 221. 1839 | |publication_place=2: 221. 1839 | ||
| Line 28: | Line 29: | ||
|elevation=0–1500 m | |elevation=0–1500 m | ||
|distribution=B.C.;Calif.;Idaho;Mont.;Oreg.;Wash. | |distribution=B.C.;Calif.;Idaho;Mont.;Oreg.;Wash. | ||
| − | |discussion=<p><i>Carex exsiccata</i> is regarded by some authors, with some justification, as <i>C. vesicaria</i> < | + | |discussion=<p><i>Carex exsiccata</i> is regarded by some authors, with some justification, as <i>C. vesicaria</i> <i></i>var.<i> major</i>. It is a coarser plant with leathery, lanceolate perigynia gradually tapered to the apex that occurs at lower elevations and is usually readily distinguishable although some plants from the Cascades are difficult to place. In the west, typical <i>C. vesicaria</i> occurs mostly above 1400 m. Some authors (B. Boivin 1967–1979; T. M. C. Taylor 1983) treat all western plants as <i>C. exsiccata</i>, distinct from the eastern North American and Eurasian <i>C. vesicaria</i>. The Rocky Mountain, Cascade Range, and Sierra <i>Nevada</i> plants do not differ substantially from eastern plants, except that sometimes they have darker perigynia and scales.</p> |
|tables= | |tables= | ||
|references= | |references= | ||
| Line 37: | Line 38: | ||
-->{{#Taxon: | -->{{#Taxon: | ||
name=Carex exsiccata | name=Carex exsiccata | ||
| − | |||
|authority=L. H. Bailey | |authority=L. H. Bailey | ||
|rank=species | |rank=species | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
|publication year=1889 | |publication year=1889 | ||
|special status= | |special status= | ||
| − | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/ | + | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/f50eec43f223ca0e34566be0b046453a0960e173/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V23/V23_942.xml |
|genus=Carex | |genus=Carex | ||
|section=Carex sect. Vesicariae | |section=Carex sect. Vesicariae | ||
Revision as of 21:12, 16 December 2019
Plants cespitose; rhizomes short or inconspicuous. Culms trigonous in cross section, 30–100 cm, scabrous-angled distally. Leaves: basal sheaths reddish purple, thickened, not spongy; ligules longer than wide; blades mid to dark green, flat to W-shaped, widest leaves 2.5–6.2 mm wide, smooth adaxially. Inflorescences 10–36 cm; proximal bract 12–55 cm, exceeding but not more than 2.5 times as long as inflorescence; proximal 2–4(–5) spikes pistillate, erect, ca. 20–150-flowered, cylindric; terminal 2–3 spikes staminate, well elevated beyond summit of separate pistillate spikes. Pistillate scales lanceolate to ovate, 2.6–5.5 × 0.8–2 mm, shorter than perigynia, margins entire, apex acute to acuminate, awnless. Perigynia ascending, often green or straw colored, strongly 9–20-veined, veins running into beak, lanceolate, 7.5–10.1 × 1.5–2.4(–2.7) mm, 3.4–5 times as long as wide, leathery, apex gradually tapered; beak indistinct, 1.5–3 mm, bidentate, smooth, teeth straight, 0.2–0.9 mm. Stigmas 3. Achenes brown, symmetric, not indented, trigonous, smooth.
Phenology: Fruiting Jun–Sep.
Habitat: Lake, pond, and river shores, marshes, sedge meadows, often in shallow water
Elevation: 0–1500 m
Distribution
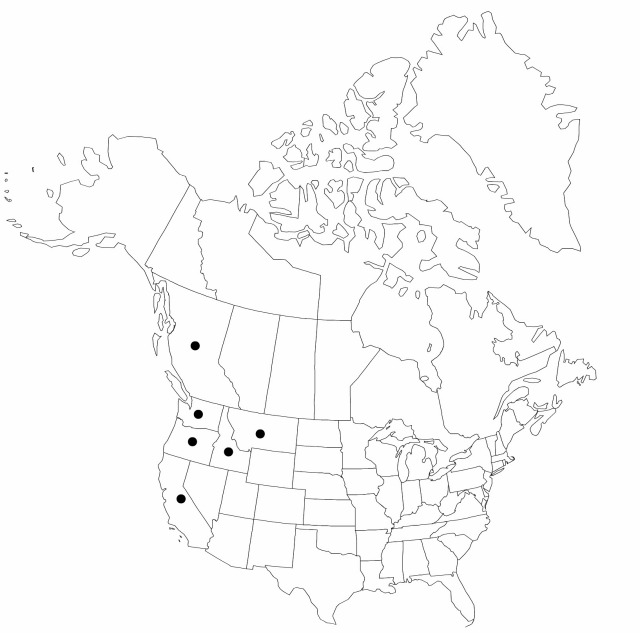
B.C., Calif., Idaho, Mont., Oreg., Wash.
Discussion
Carex exsiccata is regarded by some authors, with some justification, as C. vesicaria var. major. It is a coarser plant with leathery, lanceolate perigynia gradually tapered to the apex that occurs at lower elevations and is usually readily distinguishable although some plants from the Cascades are difficult to place. In the west, typical C. vesicaria occurs mostly above 1400 m. Some authors (B. Boivin 1967–1979; T. M. C. Taylor 1983) treat all western plants as C. exsiccata, distinct from the eastern North American and Eurasian C. vesicaria. The Rocky Mountain, Cascade Range, and Sierra Nevada plants do not differ substantially from eastern plants, except that sometimes they have darker perigynia and scales.
Selected References
None.