Difference between revisions of "Cucumis melo subsp. agrestis"
in P. M. Zhukovsky, Turquie Agric., 534. 1933.
FNA>Volume Importer |
FNA>Volume Importer |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
|special_status={{Treatment/ID/Special_status | |special_status={{Treatment/ID/Special_status | ||
|code=F | |code=F | ||
| − | |label= | + | |label=Illustrated |
}}{{Treatment/ID/Special_status | }}{{Treatment/ID/Special_status | ||
|code=I | |code=I | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
|name=Cucumis melo var. agrestis | |name=Cucumis melo var. agrestis | ||
|authority=Naudin | |authority=Naudin | ||
| + | |rank=variety | ||
|publication_title=Ann. Sci. Nat., Bot., sér. | |publication_title=Ann. Sci. Nat., Bot., sér. | ||
|publication_place=4, 11: 73. 1859 | |publication_place=4, 11: 73. 1859 | ||
| Line 36: | Line 37: | ||
|elevation=30–100(–1200) m | |elevation=30–100(–1200) m | ||
|distribution=Ont.;Ariz.;Ark.;Calif.;Conn.;Fla.;Ga.;La.;Miss.;N.C.;Okla.;Tenn.;Tex.;c;e Asia;introduced also in Mexico;West Indies;Central America;South America;Europe;se Asia (Indonesia);Africa;Pacific Islands (Marquesas Islands). | |distribution=Ont.;Ariz.;Ark.;Calif.;Conn.;Fla.;Ga.;La.;Miss.;N.C.;Okla.;Tenn.;Tex.;c;e Asia;introduced also in Mexico;West Indies;Central America;South America;Europe;se Asia (Indonesia);Africa;Pacific Islands (Marquesas Islands). | ||
| − | |discussion=<p>Wild populations (< | + | |discussion=<p>Wild populations (<i></i>subsp.<i> agrestis</i>) of <i>Cucumis melo</i> in the flora area commonly have been assumed to represent escaped forms of cultivated var. chito or var. dudaim or, less commonly, of var. agrestis. D. S. Decker et al. (2002) showed that populations in the southeastern United States are morphologically and molecularly distinct and appropriately recognized as var. texanus (Arkansas, Florida, Mississippi, Texas; Mexico). Variety texanus shows the greatest genetic affinities to var. chito and to cultivars from eastern Asia. The wild or cultivated progenitor of <i></i>subsp.<i> agrestis</i> was presumably brought to the Western Hemisphere by humans intentionally (for example, by Asian immigrants) or unintentionally (for example, as seeds mixed with those of other introduced crops), either in pre-Columbian times (given the distinctiveness of genetic differentiation) or post-Columbian.</p><!-- |
--><p>Variety dudaim is encountered outside of cultivation in California, along waterways and irrigation canals, fields, and roadsides. A collection from Sycamore Canyon in Santa Cruz County, Arizona, may be var. dudaim: Thorne 59482 (ARIZ, ASU), described as an apparently naturalized vine on the canyon bottom.</p><!-- | --><p>Variety dudaim is encountered outside of cultivation in California, along waterways and irrigation canals, fields, and roadsides. A collection from Sycamore Canyon in Santa Cruz County, Arizona, may be var. dudaim: Thorne 59482 (ARIZ, ASU), described as an apparently naturalized vine on the canyon bottom.</p><!-- | ||
| − | --><p>Main cultivar groups of < | + | --><p>Main cultivar groups of <i></i>subsp.<i> agrestis</i>:</p><!-- |
--><p>a. <i>Cucumis melo</i> var. agrestis Naudin. Africa and Asia as weeds; fruits less than 5 cm, inedible with thin mesocarp and tiny seeds; monoecious.</p><!-- | --><p>a. <i>Cucumis melo</i> var. agrestis Naudin. Africa and Asia as weeds; fruits less than 5 cm, inedible with thin mesocarp and tiny seeds; monoecious.</p><!-- | ||
--><p>b. <i>Cucumis melo</i> var. chito (C. Morren) Naudin. Asia, or reportedly of American feral origin (A. Stepansky et al. 1999); fruits plum-sized, aromatic, used as pickles; monoecious. Combined with var. dudaim by H. M. Munger and R. W. Robinson (1991).</p><!-- | --><p>b. <i>Cucumis melo</i> var. chito (C. Morren) Naudin. Asia, or reportedly of American feral origin (A. Stepansky et al. 1999); fruits plum-sized, aromatic, used as pickles; monoecious. Combined with var. dudaim by H. M. Munger and R. W. Robinson (1991).</p><!-- | ||
--><p>c. <i>Cucumis melo</i> var. conomon (Thunberg) Makino. Eastern Asia cultivars; fruits smooth, white-fleshed, with thin rinds, often eaten as pickles; andromonoecious. Includes var. acidulus Naudin.</p><!-- | --><p>c. <i>Cucumis melo</i> var. conomon (Thunberg) Makino. Eastern Asia cultivars; fruits smooth, white-fleshed, with thin rinds, often eaten as pickles; andromonoecious. Includes var. acidulus Naudin.</p><!-- | ||
--><p>d. <i>Cucumis melo</i> var. dudaim (Linnaeus) Naudin. Asia (Iran), grown as ornamentals (Dudaim melon, Queen Anne’s pocket melon, smellmelon) or for edible fruits; fruits small, aromatic, red or brown striped; andromonoecious.</p><!-- | --><p>d. <i>Cucumis melo</i> var. dudaim (Linnaeus) Naudin. Asia (Iran), grown as ornamentals (Dudaim melon, Queen Anne’s pocket melon, smellmelon) or for edible fruits; fruits small, aromatic, red or brown striped; andromonoecious.</p><!-- | ||
| − | --><p>e. <i>Cucumis melo</i> var. flexuosus (Linnaeus) Naudin. Middle East, Asia; fruits elongated, non-sweet, eaten immature as cucumbers; usually monoecious; variable in hypanthium vestiture; molecular data place it in < | + | --><p>e. <i>Cucumis melo</i> var. flexuosus (Linnaeus) Naudin. Middle East, Asia; fruits elongated, non-sweet, eaten immature as cucumbers; usually monoecious; variable in hypanthium vestiture; molecular data place it in <i></i>subsp.<i> agrestis</i>.</p><!-- |
--><p>f. <i>Cucumis melo</i> var. momordica (Roxburgh) Cogniaux. Asia (India); pepos large, non-sweet, with thin rind splitting; monoecious.</p><!-- | --><p>f. <i>Cucumis melo</i> var. momordica (Roxburgh) Cogniaux. Asia (India); pepos large, non-sweet, with thin rind splitting; monoecious.</p><!-- | ||
--><p>g. <i>Cucumis melo</i> var. texanus Naudin. North America; fruits small, rind smooth, yellow; monoecious.</p> | --><p>g. <i>Cucumis melo</i> var. texanus Naudin. North America; fruits small, rind smooth, yellow; monoecious.</p> | ||
| Line 54: | Line 55: | ||
-->{{#Taxon: | -->{{#Taxon: | ||
name=Cucumis melo subsp. agrestis | name=Cucumis melo subsp. agrestis | ||
| − | |||
|authority=(Naudin) Pangalo in P. M. Zhukovsky | |authority=(Naudin) Pangalo in P. M. Zhukovsky | ||
|rank=subspecies | |rank=subspecies | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
|publication title=in P. M. Zhukovsky, Turquie Agric., | |publication title=in P. M. Zhukovsky, Turquie Agric., | ||
|publication year=1933 | |publication year=1933 | ||
| − | |special status= | + | |special status=Illustrated;Introduced |
| − | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/ | + | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/f50eec43f223ca0e34566be0b046453a0960e173/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V6/V6_55.xml |
|genus=Cucumis | |genus=Cucumis | ||
|species=Cucumis melo | |species=Cucumis melo | ||
Revision as of 23:05, 16 December 2019
Plants monoecious or andro-monoecious. Stems retrorsely hispid. Hypanthia retrorsely or antrorsely sericeous, hairs appressed. Pepos not edible, broadly ellipsoid to subglobose, 2.5–5 cm diam., rind yellow or yellowish, sometimes orange or brown striped, smooth; flesh whitish.
Phenology: Flowering Jul–Oct(–Nov).
Habitat: Stream banks, lake shores, marsh edges, hardwood bottomlands, stream beds, sand bars, levees, spoil banks, ditch banks, dunes, clear-cut woods, fallow fields, pastures, soybean, rice, and sugarcane fields, railroad banks, abandoned homesites, vacant lots, roadsides and medians, fencerows, trash dumps, other disturbed areas.
Elevation: 30–100(–1200) m
Distribution
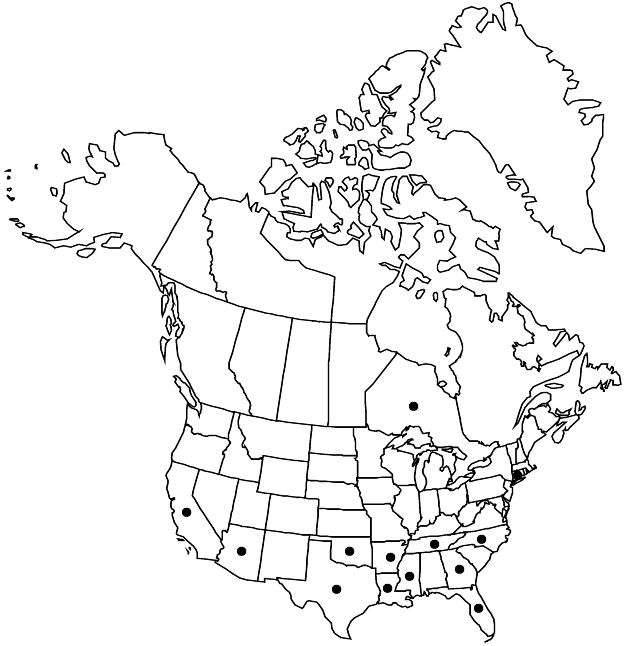
Ont., Ariz., Ark., Calif., Conn., Fla., Ga., La., Miss., N.C., Okla., Tenn., Tex., c, e Asia, introduced also in Mexico, West Indies, Central America, South America, Europe, se Asia (Indonesia), Africa, Pacific Islands (Marquesas Islands).
Discussion
Wild populations (subsp. agrestis) of Cucumis melo in the flora area commonly have been assumed to represent escaped forms of cultivated var. chito or var. dudaim or, less commonly, of var. agrestis. D. S. Decker et al. (2002) showed that populations in the southeastern United States are morphologically and molecularly distinct and appropriately recognized as var. texanus (Arkansas, Florida, Mississippi, Texas; Mexico). Variety texanus shows the greatest genetic affinities to var. chito and to cultivars from eastern Asia. The wild or cultivated progenitor of subsp. agrestis was presumably brought to the Western Hemisphere by humans intentionally (for example, by Asian immigrants) or unintentionally (for example, as seeds mixed with those of other introduced crops), either in pre-Columbian times (given the distinctiveness of genetic differentiation) or post-Columbian.
Variety dudaim is encountered outside of cultivation in California, along waterways and irrigation canals, fields, and roadsides. A collection from Sycamore Canyon in Santa Cruz County, Arizona, may be var. dudaim: Thorne 59482 (ARIZ, ASU), described as an apparently naturalized vine on the canyon bottom.
Main cultivar groups of subsp. agrestis:
a. Cucumis melo var. agrestis Naudin. Africa and Asia as weeds; fruits less than 5 cm, inedible with thin mesocarp and tiny seeds; monoecious.
b. Cucumis melo var. chito (C. Morren) Naudin. Asia, or reportedly of American feral origin (A. Stepansky et al. 1999); fruits plum-sized, aromatic, used as pickles; monoecious. Combined with var. dudaim by H. M. Munger and R. W. Robinson (1991).
c. Cucumis melo var. conomon (Thunberg) Makino. Eastern Asia cultivars; fruits smooth, white-fleshed, with thin rinds, often eaten as pickles; andromonoecious. Includes var. acidulus Naudin.
d. Cucumis melo var. dudaim (Linnaeus) Naudin. Asia (Iran), grown as ornamentals (Dudaim melon, Queen Anne’s pocket melon, smellmelon) or for edible fruits; fruits small, aromatic, red or brown striped; andromonoecious.
e. Cucumis melo var. flexuosus (Linnaeus) Naudin. Middle East, Asia; fruits elongated, non-sweet, eaten immature as cucumbers; usually monoecious; variable in hypanthium vestiture; molecular data place it in subsp. agrestis.
f. Cucumis melo var. momordica (Roxburgh) Cogniaux. Asia (India); pepos large, non-sweet, with thin rind splitting; monoecious.
g. Cucumis melo var. texanus Naudin. North America; fruits small, rind smooth, yellow; monoecious.
Selected References
None.