Difference between revisions of "Rosa palustris"
Arbust. Amer., 135. 1785.
FNA>Volume Importer |
FNA>Volume Importer |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
|name=Rosa floridana | |name=Rosa floridana | ||
|authority=Rydberg | |authority=Rydberg | ||
| − | }}{{Treatment/ID/Synonym | + | }} {{Treatment/ID/Synonym |
|name=R. gemella | |name=R. gemella | ||
|authority=Willdenow | |authority=Willdenow | ||
| − | }}{{Treatment/ID/Synonym | + | }} {{Treatment/ID/Synonym |
|name=R. lancifolia | |name=R. lancifolia | ||
|authority=Small | |authority=Small | ||
| − | }}{{Treatment/ID/Synonym | + | }} {{Treatment/ID/Synonym |
|name=R. obtusiuscula | |name=R. obtusiuscula | ||
|authority=Rydberg | |authority=Rydberg | ||
| − | }}{{Treatment/ID/Synonym | + | }} {{Treatment/ID/Synonym |
|name=R. palustris var. dasistema | |name=R. palustris var. dasistema | ||
|authority=(Rafinesque) E. J. Palmer & Steyermark | |authority=(Rafinesque) E. J. Palmer & Steyermark | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
|elevation=0–700 m | |elevation=0–700 m | ||
|distribution=N.B.;N.S.;Ont.;Que.;Ala.;Ark.;Conn.;Del.;D.C.;Fla.;Ga.;Ill.;Ind.;Iowa;Ky.;Maine;Md.;Mass.;Mich.;Miss.;Mo.;N.H.;N.J.;N.Y.;N.C.;Ohio;Pa.;R.I.;S.C.;Tenn.;Vt.;Va.;W.Va.;Wis.;introduced in Europe. | |distribution=N.B.;N.S.;Ont.;Que.;Ala.;Ark.;Conn.;Del.;D.C.;Fla.;Ga.;Ill.;Ind.;Iowa;Ky.;Maine;Md.;Mass.;Mich.;Miss.;Mo.;N.H.;N.J.;N.Y.;N.C.;Ohio;Pa.;R.I.;S.C.;Tenn.;Vt.;Va.;W.Va.;Wis.;introduced in Europe. | ||
| − | |discussion=<p>The single 1952 collection of Rosa palustris from Lake of Three Fires State Park (ISC), Taylor County, southwestern Iowa, is about 430 km northwest of the nearest known collection of the species, in Missouri. The species was probably introduced. It has the most serrulate leaflet margins of all roses in North America; the stems usually have short, stout, curved infrastipular prickles, rarely without armature.</p><!-- | + | |discussion=<p>The single 1952 collection of <i>Rosa palustris</i> from Lake of Three Fires State Park (ISC), Taylor County, southwestern Iowa, is about 430 km northwest of the nearest known collection of the species, in Missouri. The species was probably introduced. It has the most serrulate leaflet margins of all roses in North America; the stems usually have short, stout, curved infrastipular prickles, rarely without armature.</p><!-- |
| − | --><p>Rosa ×palustriformis (Rydberg) Voss (R. carolina var. aculeata Schuette, R. michiganensis Erlanson, R. schuetteana Erlanson) refers to putative hybrids between R. blanda × R. palustris from Maine, Michigan, Ohio, and Wisconsin. Rosa schuetteana is morphologically intermediate between the parental species; R. ×palustriformis is more similar to R. palustris. Rosa blanda and R. palustris differ by: branch armature (R. blanda unarmed or with sparse prickles or aciculi, R. palustris with stout, curved infrastipular prickles or unarmed); length of each auricle (R. blanda average 4.8 mm, R. palustris average 2.6 mm); petioles and rachises with pricklets (R. blanda rare, R. palustris common); leaflet serrations (R. blanda serrate, acute, teeth 10–26 per blade side, R. palustris serrulate, slightly blunt, teeth 20–30 per blade side); pedicels stipitate-glandular (R. blanda eglandular, R. palustris almost always); hypanthia stipitate-glandular (R. blanda eglandular, R. palustris almost always); inflorescences corymbs (R. blanda rare, R. palustris common).</p><!-- | + | --><p><i>Rosa</i> ×palustriformis (Rydberg) Voss (<i>R. carolina</i> <i></i>var.<i> aculeata</i> Schuette, R. michiganensis Erlanson, R. schuetteana Erlanson) refers to putative hybrids between <i>R. blanda</i> × <i>R. palustris</i> from Maine, Michigan, Ohio, and Wisconsin. <i>Rosa</i> schuetteana is morphologically intermediate between the parental species; R. ×palustriformis is more similar to <i>R. palustris</i>. <i>Rosa blanda</i> and <i>R. palustris</i> differ by: branch armature (<i>R. blanda</i> unarmed or with sparse prickles or aciculi, <i>R. palustris</i> with stout, curved infrastipular prickles or unarmed); length of each auricle (<i>R. blanda</i> average 4.8 mm, <i>R. palustris</i> average 2.6 mm); petioles and rachises with pricklets (<i>R. blanda</i> rare, <i>R. palustris</i> common); leaflet serrations (<i>R. blanda</i> serrate, acute, teeth 10–26 per blade side, <i>R. palustris</i> serrulate, slightly blunt, teeth 20–30 per blade side); pedicels stipitate-glandular (<i>R. blanda</i> eglandular, <i>R. palustris</i> almost always); hypanthia stipitate-glandular (<i>R. blanda</i> eglandular, <i>R. palustris</i> almost always); inflorescences corymbs (<i>R. blanda</i> rare, <i>R. palustris</i> common).</p><!-- |
| − | --><p>Root decoctions of Rosa palustris were drunk by Cherokee to treat diarrhea (W. H. Lewis and M. P. F. Elvin-Lewis 2003). In Maine, R. palustris hips, including their achenes, are gathered about February, flattened, dried, and ground into flour for use with ground wheat to make leavened bread. The bread has a red color and a fine taste reminiscent of tomatoes (Arthur Haines, pers. comm.).</p> | + | --><p>Root decoctions of <i>Rosa palustris</i> were drunk by Cherokee to treat diarrhea (W. H. Lewis and M. P. F. Elvin-Lewis 2003). In Maine, <i>R. palustris</i> hips, including their achenes, are gathered about February, flattened, dried, and ground into flour for use with ground wheat to make leavened bread. The bread has a red color and a fine taste reminiscent of tomatoes (Arthur Haines, pers. comm.).</p> |
|tables= | |tables= | ||
|references= | |references= | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
|publication year=1785 | |publication year=1785 | ||
|special status=Endemic;Selected by author to be illustrated | |special status=Endemic;Selected by author to be illustrated | ||
| − | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/ | + | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/8f726806613d60c220dc4493de13607dd3150896/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V9/V9_145.xml |
|subfamily=Rosaceae subfam. Rosoideae | |subfamily=Rosaceae subfam. Rosoideae | ||
|tribe=Rosaceae tribe Roseae | |tribe=Rosaceae tribe Roseae | ||
Revision as of 19:15, 18 September 2019
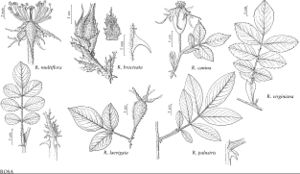
Shrubs, forming thickets. Stems erect, 10–25(–30) dm, sparsely branched; bark reddish brown, glabrous; infrastipular prickles paired, curved, rarely erect, stout, 3.5–8 × 2–5(–10) mm, base glabrous, internodal prickles and aciculi rare, sometimes absent. Leaves 8–11 cm; stipules narrow, 10–22(–35) × 2.5–4 mm, auricles erect, rarely flared, 2.5–4.5(–8) mm, margins serrulate, eglandular or stipitate-glandular, surfaces glabrous, eglandular; petiole and rachis usually with pricklets, puberulent to pubescent, sometimes glabrous, eglandular or sparsely stipitate-glandular; leaflets 5–7, terminal: petiolule 5–10 mm, blade ovate-lanceolate, rarely broadly lanceolate or narrowly elliptic, 23–45 × 10–18 mm, membranous, base cuneate, margins 1–2-serrulate, eglandular, teeth 20–30 per side, acute to ± obtuse, eglandular, apex acute to subacute, abaxial surfaces pale green, glabrous or pubescent, eglandular, adaxial green, dull, glabrous. Inflorescences corymbs, (1 or)2–10(–40)-flowered. Pedicels erect, slender, 6–15 mm, glabrous, densely stipitate-glandular; bracts 2, lanceolate, 6–15 × 3–4 mm, margins and central veins pubescent, eglandular, surfaces pubescent, eglandular. Flowers 2.5–5 cm diam.; hypanthium cupulate, 2–4 × 2–4 mm, glabrous, sparsely to densely stipitate-glandular, neck absent or 1–3 mm; sepals spreading to reflexed, rarely erect, lanceolate to narrowly ovate-lanceolate, 15–30(–40) × 2–3.5 mm, tip 2.5–3.5 × 0.5–1 mm, margins entire, rarely pinnate, abaxial surfaces glabrous, densely, sometimes sparsely, stipitate-glandular; petals single, pink to deep pink, 14–28 × 13–28 mm; stamens 200; carpels 24–50, styles exsert 0.5–1 m beyond stylar orifice (1.5 mm diam.) of hypanthial disc (3.5–4.5 mm diam.). Hips deep red, usually globose to subglobose, rarely elongate, 7–11 × 7–11 mm, fleshy, glabrous, sparsely or densely stipitate-glandular, neck absent or 3 × 1 mm; sepals deciduous, spreading. Achenes basal, 26, tan, 3 × 1.5–2 mm. 2n = 14.
Phenology: Flowering (Jun–)Jul(–Aug).
Habitat: Swampy woods and pastures, marshes, edges of ponds, springs, lakes, backwaters, sloughs, streams, ditches
Elevation: 0–700 m
Distribution
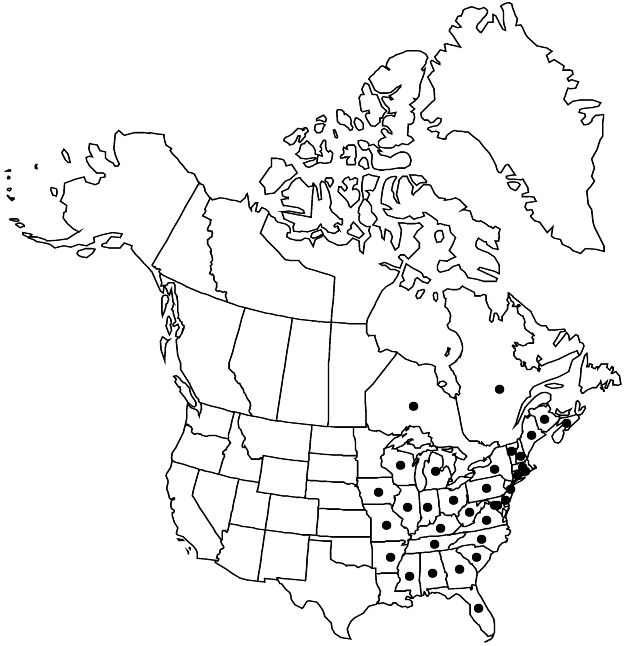
N.B., N.S., Ont., Que., Ala., Ark., Conn., Del., D.C., Fla., Ga., Ill., Ind., Iowa, Ky., Maine, Md., Mass., Mich., Miss., Mo., N.H., N.J., N.Y., N.C., Ohio, Pa., R.I., S.C., Tenn., Vt., Va., W.Va., Wis., introduced in Europe.
Discussion
The single 1952 collection of Rosa palustris from Lake of Three Fires State Park (ISC), Taylor County, southwestern Iowa, is about 430 km northwest of the nearest known collection of the species, in Missouri. The species was probably introduced. It has the most serrulate leaflet margins of all roses in North America; the stems usually have short, stout, curved infrastipular prickles, rarely without armature.
Rosa ×palustriformis (Rydberg) Voss (R. carolina var. aculeata Schuette, R. michiganensis Erlanson, R. schuetteana Erlanson) refers to putative hybrids between R. blanda × R. palustris from Maine, Michigan, Ohio, and Wisconsin. Rosa schuetteana is morphologically intermediate between the parental species; R. ×palustriformis is more similar to R. palustris. Rosa blanda and R. palustris differ by: branch armature (R. blanda unarmed or with sparse prickles or aciculi, R. palustris with stout, curved infrastipular prickles or unarmed); length of each auricle (R. blanda average 4.8 mm, R. palustris average 2.6 mm); petioles and rachises with pricklets (R. blanda rare, R. palustris common); leaflet serrations (R. blanda serrate, acute, teeth 10–26 per blade side, R. palustris serrulate, slightly blunt, teeth 20–30 per blade side); pedicels stipitate-glandular (R. blanda eglandular, R. palustris almost always); hypanthia stipitate-glandular (R. blanda eglandular, R. palustris almost always); inflorescences corymbs (R. blanda rare, R. palustris common).
Root decoctions of Rosa palustris were drunk by Cherokee to treat diarrhea (W. H. Lewis and M. P. F. Elvin-Lewis 2003). In Maine, R. palustris hips, including their achenes, are gathered about February, flattened, dried, and ground into flour for use with ground wheat to make leavened bread. The bread has a red color and a fine taste reminiscent of tomatoes (Arthur Haines, pers. comm.).
Selected References
None.