familySelaginellaceae
genusSelaginella
speciesSelaginella arenicola
subspeciesSelaginella arenicola subsp. arenicola
Difference between revisions of "Selaginella arenicola subsp. arenicola"
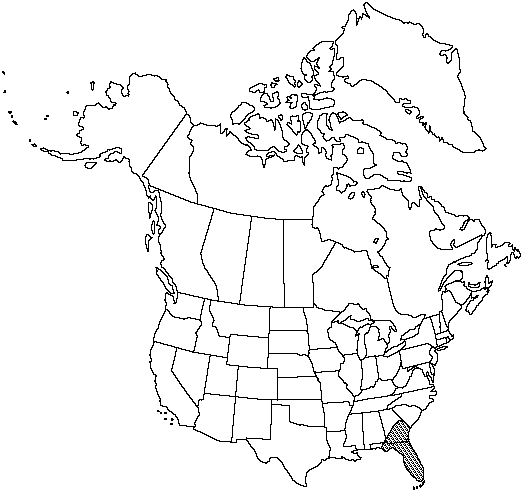
Endemic
Treatment appears in FNA Volume 2.
imported>Volume Importer |
imported>Volume Importer |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
|publication year= | |publication year= | ||
|special status=Endemic | |special status=Endemic | ||
| − | |source xml=https:// | + | |source xml=https://bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation/src/2e0870ddd59836b60bcf96646a41e87ea5a5943a/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V2/V2_64.xml |
|genus=Selaginella | |genus=Selaginella | ||
|subgenus=Selaginella subg. Tetragonostachys | |subgenus=Selaginella subg. Tetragonostachys | ||
Latest revision as of 21:24, 5 November 2020
Leaves (aerial stems) usually tightly appressed; base conspicuously pubescent. Strobili sometimes with apical vegetative growth, distinctly larger in diameter than subtending stem. Sporophylls abruptly tapering toward apex; apex often recurved.
Habitat: Mostly on dry, exposed sand dunes, white sand, or sandy soil
Elevation: 0 m
Discussion
Selaginella arenicola subsp. arenicola usually has more slender (1 mm diam.) stems than subsp. riddelli (stems more than 1 mm diam.). In Georgia, many forms intermediate between the two subspecies have been reported.
Selected References
None.
Lower Taxa
None.