Difference between revisions of "Setaria sphacelata"
FNA>Volume Importer |
FNA>Volume Importer |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
-->{{Treatment/Body | -->{{Treatment/Body | ||
|distribution=Calif.;Fla.;Ala.;Miss. | |distribution=Calif.;Fla.;Ala.;Miss. | ||
| − | |discussion=<p><i>Setaria sphacelata</i> is native to tropical Africa, but it has been found at a few scattered locations in the Flora region, often near a port. Clayton (1979) recognized five varieties of <i>Setaria sphacelata</i>. Those most likely to be introduced into the United States are <i>Setaria</i> sphace¬lata (Schumach.) Stapf & C.E. Hubb. var. sphacelata and <i>S. sphacelata</i> <i></i>var.<i> aurea</i> (Hochst. ex A. Braun) Clayton, with <i></i>var.<i> aurea</i> differing from var. sphacelata in having fibrous basal leaf sheaths and upper glumes that are often 3-veined.</p> | + | |discussion=<p><i>Setaria sphacelata</i> is native to tropical Africa, but it has been found at a few scattered locations in the Flora region, often near a port. Clayton (1979) recognized five varieties of <i>Setaria sphacelata</i>. Those most likely to be introduced into the United States are <i>Setaria</i> sphace¬lata (Schumach.) Stapf & C.E. Hubb. var. sphacelata and <i>S. sphacelata</i> <i></i></i>var.<i><i> aurea</i> (Hochst. ex A. Braun) Clayton, with <i></i></i>var.<i><i> aurea</i> differing from var. sphacelata in having fibrous basal leaf sheaths and upper glumes that are often 3-veined.</p> |
|tables= | |tables= | ||
|references= | |references= | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
|publication year= | |publication year= | ||
|special status= | |special status= | ||
| − | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/ | + | |source xml=https://jpend@bitbucket.org/aafc-mbb/fna-data-curation.git/src/f6b125a955440c0872999024f038d74684f65921/coarse_grained_fna_xml/V25/V25_1424.xml |
|subfamily=Poaceae subfam. Panicoideae | |subfamily=Poaceae subfam. Panicoideae | ||
|tribe=Poaceae tribe Paniceae | |tribe=Poaceae tribe Paniceae | ||
Revision as of 20:23, 24 September 2019
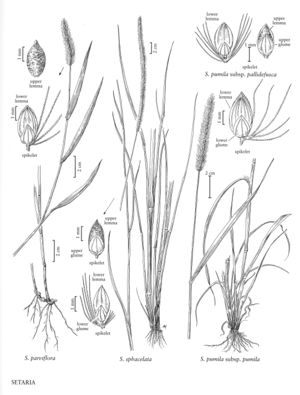
Plants perennial; cespitose, rhizomatous, rhizomes stout. Culms 50-150 cm, flattened; nodes glabrous. Sheaths glabrous; blades 15-50 cm long, 4-10 mm wide, flat, rather lax. Panicles 5-25 cm long, 4-8 mm thick (excluding the bristles), densely spicate; bristles 5 or more, 3-6 mm, usually orange to purple. Spikelets 2.5-3 mm, elliptic-oblong. Lower glumes about as long as the spikelets; upper florets staminate; upper glumes Vi-A as long as the spikelets; lower lemmas equaling the upper lemmas; lower paleas equaling the upper paleas, broad; upper lemmas finely and transversely rugose; upper paleas similar to the upper lemmas. 2n = 36, 54.
Distribution
Calif., Fla., Ala., Miss.
Discussion
Setaria sphacelata is native to tropical Africa, but it has been found at a few scattered locations in the Flora region, often near a port. Clayton (1979) recognized five varieties of Setaria sphacelata. Those most likely to be introduced into the United States are Setaria sphace¬lata (Schumach.) Stapf & C.E. Hubb. var. sphacelata and S. sphacelata var. aurea (Hochst. ex A. Braun) Clayton, with var. aurea differing from var. sphacelata in having fibrous basal leaf sheaths and upper glumes that are often 3-veined.
Selected References
None.